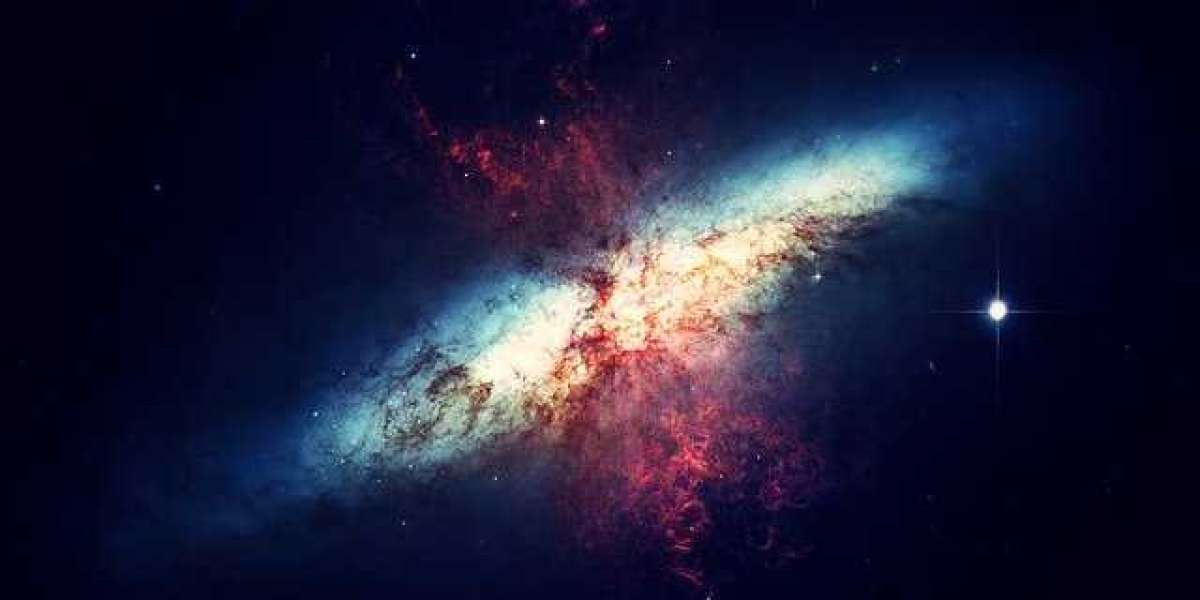
European scientists have identified the largest galaxy ever viewed by human eyes, according to reports. The Alcyoneus Galaxy, named after a Greek giant who was killed by the hero Hercules, is approximately 16.3 million light-years across, making it four times larger than the previous record holder, IC 1101, which has a diameter of 3.9 million light-years. The galaxy is about 16.3 million light-years across, making it four times larger than the previous record holder, IC 1101.
The radio radiation emitted by a black hole in the center of Alcyoneus was recorded by astronomers using the LOFAR telescope, which is a pan-European facility. The radio galaxy gets its name from the vast amount of radio energy that it emits, which gives it its astronomical description.
The radio galaxy is characterized by the presence of a black hole at its center, which ejects material into space at a rate that is on the verge of exceeding the speed of light. Speed generates so much heat that stardust disintegrates into plasma, resulting in a visible glow, also known as radio light.
The finding of Alcyoneus also prompted fresh questions concerning the expansion of galaxies and how they are formed. According to the team of scientists that discovered it, Alcyoneus is a pretty ordinary galaxy that is distinguished only by its huge size.
Alcyoneus and its host galaxy are suspiciously ordinary in terms of their physical characteristics: their total low-frequency light density, stellar mass, and supermassive black hole mass are all lower than those of medium-sized giant radio galaxies, though they are similar to those of medium-sized giant radio galaxies, according to European astronomers. Their findings are available on the arXiv repository and are awaiting scientific review.
When astronomers discovered a big galaxy with "ordinary" properties, they were allowed to guess and carry on with their investigations. The planet Alcyoneus is believed to be in a low-density environment, according to one theory, and to be located among the strands of the cosmic network, according to another.
While issues regarding the Alcyoneus galaxy will continue to be investigated, the finding provided astronomers with new insights into the nature of the universe.
The researchers point out that "very massive galaxies or central black holes are not required for the growth of enormous giants, and if the observed condition is representative of the source during its lifetime, no significant radio power is required."